Paediatric Ophthalmology
A New “Ground-Breaking” Treatment for Amblyopia
Dichoptic therapy could improve visual acuity and stereopsis.

Priscilla Lynch
Published: Monday, October 2, 2023
“ We’ve seen remarkable results not only in improving vision in the lazy eye, but also in the brain using both eyes together. “
A specialised “brain-training” computer program has emerged as a highly effective treatment for correcting amblyopia and improving vision, even in adult eyes, according to Dr Arthur Cummings.
amblyopia and improving vision, even in adult eyes, according to Dr Arthur Cummings.
“Dichoptic therapy for amblyopia is absolutely game-changing,” he told EuroTimes. “The way it works is fascinating yet very simple, but it is a very big paradigm shift for people to understand.”
The company Bynocs, for which Dr Cummings is an advisor, has created a vision therapy software programme (AmblyGo) to treat amblyopia in the form of tailored computer games. The patient plays the games with both eyes open while wearing special 3D anaglyph glasses (with different colour lenses) for 30 minutes over 30 sessions.
 “We’ve seen remarkable results not only in improving vision in the lazy eye, but also in the brain using both eyes together,” he said.
“We’ve seen remarkable results not only in improving vision in the lazy eye, but also in the brain using both eyes together,” he said.
How it works
Traditional treatment for “lazy eye” involves patching the “good eye” in younger children for months or years. Atropine drops are another means of occlusion therapy. A landmark study by the Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group (PEDIG) showed as little as two hours of patching a day, or atropine drops during the weekend, were as effective as more intensive therapy.1
Until now, untreated or unsuccessfully treated adults with amblyopia had no option to improve vision in either eye, as procedures like laser eye surgery remained unavailable due to the risk of damaging vision in the dominant eye, Dr Cummings noted.
However, this is no longer the case with the advent of dichoptic treatment—a visual training process involving the presentation of simultaneous and separate visual stimuli to both eyes.
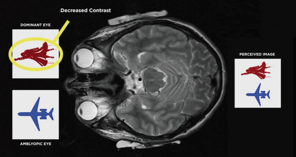
The Bynocs vision therapy software presents the contrast-adjusted images to the two eyes, with the dominant eye receiving an image of lesser contrast than the amblyopic eye. For possibly the first time ever, the brain receives an equal image from the two eyes during the therapy, encouraging it to use both eyes at the same time.
This contrast differentiation removes the interocular suppression in the ocular dominance columns in the amblyopic eye, resulting in a sustained visual gain. The neuroadaptive treatment is non-invasive, safe, and very effective, Dr Cummings said.
Research data
Dr Cummings outlined the results of 45 amblyopia patients treated in his clinic with dichoptic therapy, with an age range of 13 to 65 years, noting this age group would not have had any therapy or treatment available to them previously.
Visual acuity and stereopsis were measured before and after a six-week duration of dichoptic treatment.
Of the 45 patients, 20 had anisometropic amblyopia (the category of amblyopia that does best with dichoptic therapy)—13 had no stereopsis prior to therapy and 11 developed stereopsis during. Seven patients had some stereopsis before therapy, and all improved their stereopsis. Patients gained between 3 and 5 lines of CVDA in the amblyopic eye.
The results show dichoptic therapy is very effective in improving visual acuity and stereopsis in adult amblyopia, especially when caused by anisometropia, Dr Cummings said.
“It is very exciting. Ideally, within 10 to 15 years, this will be the definitive treatment for amblyopia in children, too, once the success in adults becomes more common knowledge. Why would a child not rather play a video game than wear a patch?”
Dr Cummings presented his findings at the Irish College of Ophthalmologists 2023 annual conference in Killarney, Ireland.
For citation notes, see page 40.
Arthur B Cummings MD, FRCSed, FWRCS is Medical Director at the Wellington Eye Clinic, Dublin, Ireland. ABC@WellingtonEyeClinic.com