Retinal dystrophies
Classifying and identifying retinal dystrophies can be difficult but necessary

Soosan Jacob
Published: Monday, March 1, 2021
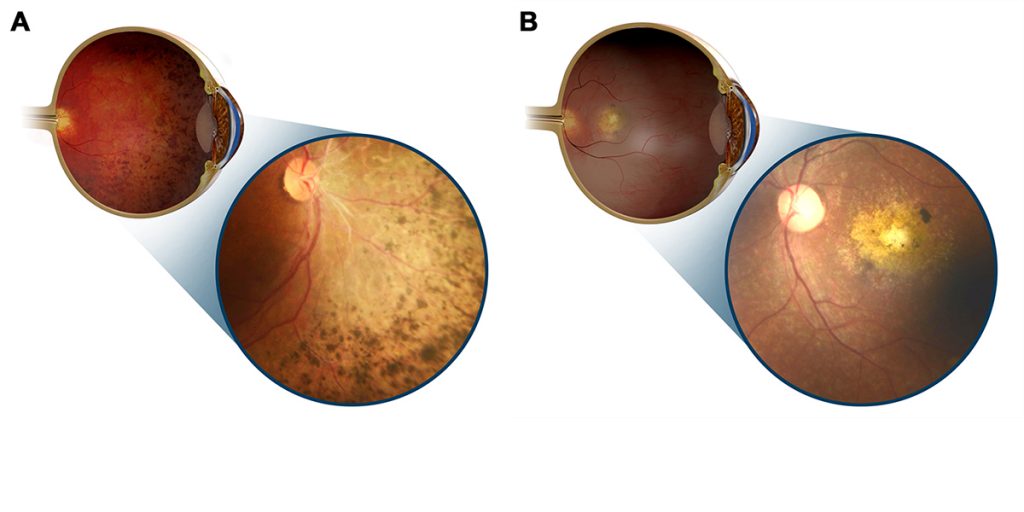 Illustrations and inset images showing retinal dystrophy with predominant mid-peripheral (A) and central (B) involvement[/caption]
Retinal dystrophies (RD) present with visual loss ranging from night blindness, colour blindness, constricted fields, central scotomata to complete blindness. Affecting about one in 4,000 individuals, they may or may not be associated with syndromic manifestations. Mutations in more than 120 genes coding for proteins present or involved in retinal cells, rods and cones, phototransduction, visual cycle or gene regulation may be causative. Mutations within the same gene and even within the same family cause different phenotypic manifestations.
Inheritance is seen in all forms: autosomal dominant, recessive, X-linked as well as mitochondrial or digenic with sporadic cases also occurring. Genetic overlap may be seen between different non-syndromic RD.
Next-generation sequencing and chromosome microarrays provide better diagnostic abilities and pave the way for genetic counselling, pre-natal diagnostics and therapy. Family history, proper phenotyping, electroretinogram (ERG), electrooculogram, dark adaptometry, colour vision, fundus autofluorescence imaging, spectral domain OCT (SD-OCT) and autoperimetry are helpful.
RD can be classified as rod-dominated, cone-dominated and generalised dystrophies.
ROD-DOMINATED RETINAL DYSTROPHIES
A genetically diverse group of disorders, these predominantly or first affect rods. Progressive (retinitis pigmentosa, RP) or stationary (Congenital Stationary Night Blindness, CSNB) forms occur. Patients with Retinitis Pigmentosa have early or late-onset progressive night blindness. Constricted fields and tunnel vision may progress to complete blindness if cones are also involved in the late stages. Retinal arteriolar attenuation, bone spicule intra-retinal pigmentary changes, waxy pale disc, tessellated fundus, unmasking of large choroidal vessels and sometimes atrophic or cellophane maculopathy and cystoid macular oedema (CME) are seen. A golden metallic tapetal sheen may be seen in female carriers of X-linked disease. Posterior subcapsular cataract, high myopia, astigmatism, keratoconus and glaucoma are associated with RP. ERG shows reduced scotopic and combined responses progressing to decreased photopic responses and finally extinguished waves. Large ERG amplitudes imply good prognosis for retention of central vision. SD-OCT shows decreased ONL thickness and loss of ELM and IS/OS junctions and correlates with microperimetry and multifocal ERG. SD-OCT is also used to evaluate CME and epiretinal membranes. Syndromic associations such as Bassen-Kornzweig, Refsum, Kearns-Sayre and Bardet-Biedl syndromes are seen. Regular visual assessment is required for RP patients who drive.
Congenital Stationary Night Blindness shows autosomal dominant, recessive, incomplete and complete form of X-linked inheritance. Affected patients have non-progressive nyctalopia, decreased vision, nystagmus, strabismus, myopia, photophobia and colour vision impairment. Two variants exist – with normal fundus (Nougaret, Schubert-Bornschein and Riggs-types) and with abnormal fundus (fundus albipunctatus and Oguchi’s disease). Mizuo-Nakamura phenomenon refers to a golden sheen that disappears after a prolonged period of dark adaptation and is seen in Oguchi’s disease. There is currently no specific treatment for CSNB, though 9-cis retinal has been tried to potentially stabilise photoreceptors.
CONE-DOMINATED RETINAL DYSTROPHIES
These result in loss of central vision and colour vision and therefore are more severe. Progressive cone (COD) or cone-rod dystrophy (CORD) are rare but may occur sporadically or with autosomal dominant, recessive or X-linked inheritance patterns. Presenting in the first to second decades, patients with CORD worsen further when rod involvement also starts. Macular atrophy or pigment deposits are seen. ERG shows decrease in photopic response and flicker fusion frequency. Stationary cone dystrophy results in complete or incomplete achromatopsia with loss of all colour perception or of only specific colours.
GENERALISED DYSTROPHY
Simultaneous involvement of both rod and cone receptors is seen, often associated with progressive and severe involvement of visual functions. Leber’s congenital amaurosis (LCA) has onset at birth or within the first year of life and has very poor visual prognosis. Nystagmus, severe visual loss and absent responses on ERG are seen. An initially normal fundus may progress to macular pigmentation, peripheral chorioretinal atrophy, mild pigmentary retinopathy, arteriolar attenuation and other changes. Repeated poking of the eyes is called the Franschetti’s oculo-digital sign. ERG is generally non-recordable. Intellectual disability, deafness and other systemic associations may be seen. Choroideremia is X-linked and shows progressive, diffuse degeneration of the choroid, RPE and retinal photoreceptors. Patients present in the first decade with night blindness and generally have severe visual loss after about 50 years of age.
MACULAR DYSTROPHY
This refers to a group of conditions with Mendelian inheritance, pathology limited to the eye and with bilateral and generally very symmetrical macular lesions. It includes Best, Stargardt, PROM-1 associated disease, Sorsby, pattern dystrophy and others. When considering macular dystrophy, neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis and drug toxicity should be ruled out by appropriate history and investigations.
TREATMENT
Corrective lenses, low-vision aids, disease course as well as genetic counselling, occupational and psychosocial support are necessary. Different filtered contact lenses, e.g., low light transmitting orange or red for achromatopsia and blue light filtering sunglasses for Stargardt may help. Drugs that modulate the visual cycle such as isotretinoin and fenretinide may be used in some conditions. Though a nutritious and well-balanced diet is recommended, there is no clear consensus. High-dose Vitamin A and carotenoids may modestly slow progression of RP; however, it is not recommended because of lack of definite evidence and possible toxicity. Vitamin A should be avoided by patients with Best and Stargardt dystrophies as it may cause exacerbation by increasing formation of bisretinoids. Vitamin E supplementation is beneficial in Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome with neurological manifestations. Plasmapheresis and a phytanic-acid-free diet is advised in Refsum disease. An arginine-restricted diet and oral Vitamin B6 supplementation is used in gyrate atrophy. Acetazolamide may be used for CME associated with RP. Anti-VEGF therapy may be given for choroidal neovascular membranes in Best, Sorsby fundus dystrophy etc.
Newer treatment strategies directed towards stem cell and gene-based treatments are in trials. Luxturna (Spark Therapeutics) provides RPE65gene replacement therapy delivered by viral vectors to restore the visual cycle in children with early stage LCA and has shown promise. Functional cDNA has also been delivered to the retina via viral vectors. With advanced disease or extensive involvement, gene therapy is not effective and pluripotent stem cell transplants or retinal implants may be tried. Subretinal transplantation or intravitreal injections of human embryonic stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelial cells, autologous bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells, undifferentiated umbilical cells etc. are under trial. Application of CRISPR technology with stem cells may allow individualised and targeted treatment.
Retinal prosthetics, e.g., light-sensing microchips are implanted into the retina and transmit impulses via the remaining neural network to the brain. The Argus II Retinal Prosthetic System is one such example. These are used in advanced cases and have had success in restoring some visual perception or improvement in light detection. An intraocular implant releasing ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) has been tried for CSNB.
Dr Soosan Jacob is Director and Chief of Dr Agarwal's Refractive and Cornea Foundation at Dr Agarwal's Eye Hospital, Chennai, India and can be reached at dr_soosanj@hotmail.com
Illustrations and inset images showing retinal dystrophy with predominant mid-peripheral (A) and central (B) involvement[/caption]
Retinal dystrophies (RD) present with visual loss ranging from night blindness, colour blindness, constricted fields, central scotomata to complete blindness. Affecting about one in 4,000 individuals, they may or may not be associated with syndromic manifestations. Mutations in more than 120 genes coding for proteins present or involved in retinal cells, rods and cones, phototransduction, visual cycle or gene regulation may be causative. Mutations within the same gene and even within the same family cause different phenotypic manifestations.
Inheritance is seen in all forms: autosomal dominant, recessive, X-linked as well as mitochondrial or digenic with sporadic cases also occurring. Genetic overlap may be seen between different non-syndromic RD.
Next-generation sequencing and chromosome microarrays provide better diagnostic abilities and pave the way for genetic counselling, pre-natal diagnostics and therapy. Family history, proper phenotyping, electroretinogram (ERG), electrooculogram, dark adaptometry, colour vision, fundus autofluorescence imaging, spectral domain OCT (SD-OCT) and autoperimetry are helpful.
RD can be classified as rod-dominated, cone-dominated and generalised dystrophies.
ROD-DOMINATED RETINAL DYSTROPHIES
A genetically diverse group of disorders, these predominantly or first affect rods. Progressive (retinitis pigmentosa, RP) or stationary (Congenital Stationary Night Blindness, CSNB) forms occur. Patients with Retinitis Pigmentosa have early or late-onset progressive night blindness. Constricted fields and tunnel vision may progress to complete blindness if cones are also involved in the late stages. Retinal arteriolar attenuation, bone spicule intra-retinal pigmentary changes, waxy pale disc, tessellated fundus, unmasking of large choroidal vessels and sometimes atrophic or cellophane maculopathy and cystoid macular oedema (CME) are seen. A golden metallic tapetal sheen may be seen in female carriers of X-linked disease. Posterior subcapsular cataract, high myopia, astigmatism, keratoconus and glaucoma are associated with RP. ERG shows reduced scotopic and combined responses progressing to decreased photopic responses and finally extinguished waves. Large ERG amplitudes imply good prognosis for retention of central vision. SD-OCT shows decreased ONL thickness and loss of ELM and IS/OS junctions and correlates with microperimetry and multifocal ERG. SD-OCT is also used to evaluate CME and epiretinal membranes. Syndromic associations such as Bassen-Kornzweig, Refsum, Kearns-Sayre and Bardet-Biedl syndromes are seen. Regular visual assessment is required for RP patients who drive.
Congenital Stationary Night Blindness shows autosomal dominant, recessive, incomplete and complete form of X-linked inheritance. Affected patients have non-progressive nyctalopia, decreased vision, nystagmus, strabismus, myopia, photophobia and colour vision impairment. Two variants exist – with normal fundus (Nougaret, Schubert-Bornschein and Riggs-types) and with abnormal fundus (fundus albipunctatus and Oguchi’s disease). Mizuo-Nakamura phenomenon refers to a golden sheen that disappears after a prolonged period of dark adaptation and is seen in Oguchi’s disease. There is currently no specific treatment for CSNB, though 9-cis retinal has been tried to potentially stabilise photoreceptors.
CONE-DOMINATED RETINAL DYSTROPHIES
These result in loss of central vision and colour vision and therefore are more severe. Progressive cone (COD) or cone-rod dystrophy (CORD) are rare but may occur sporadically or with autosomal dominant, recessive or X-linked inheritance patterns. Presenting in the first to second decades, patients with CORD worsen further when rod involvement also starts. Macular atrophy or pigment deposits are seen. ERG shows decrease in photopic response and flicker fusion frequency. Stationary cone dystrophy results in complete or incomplete achromatopsia with loss of all colour perception or of only specific colours.
GENERALISED DYSTROPHY
Simultaneous involvement of both rod and cone receptors is seen, often associated with progressive and severe involvement of visual functions. Leber’s congenital amaurosis (LCA) has onset at birth or within the first year of life and has very poor visual prognosis. Nystagmus, severe visual loss and absent responses on ERG are seen. An initially normal fundus may progress to macular pigmentation, peripheral chorioretinal atrophy, mild pigmentary retinopathy, arteriolar attenuation and other changes. Repeated poking of the eyes is called the Franschetti’s oculo-digital sign. ERG is generally non-recordable. Intellectual disability, deafness and other systemic associations may be seen. Choroideremia is X-linked and shows progressive, diffuse degeneration of the choroid, RPE and retinal photoreceptors. Patients present in the first decade with night blindness and generally have severe visual loss after about 50 years of age.
MACULAR DYSTROPHY
This refers to a group of conditions with Mendelian inheritance, pathology limited to the eye and with bilateral and generally very symmetrical macular lesions. It includes Best, Stargardt, PROM-1 associated disease, Sorsby, pattern dystrophy and others. When considering macular dystrophy, neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis and drug toxicity should be ruled out by appropriate history and investigations.
TREATMENT
Corrective lenses, low-vision aids, disease course as well as genetic counselling, occupational and psychosocial support are necessary. Different filtered contact lenses, e.g., low light transmitting orange or red for achromatopsia and blue light filtering sunglasses for Stargardt may help. Drugs that modulate the visual cycle such as isotretinoin and fenretinide may be used in some conditions. Though a nutritious and well-balanced diet is recommended, there is no clear consensus. High-dose Vitamin A and carotenoids may modestly slow progression of RP; however, it is not recommended because of lack of definite evidence and possible toxicity. Vitamin A should be avoided by patients with Best and Stargardt dystrophies as it may cause exacerbation by increasing formation of bisretinoids. Vitamin E supplementation is beneficial in Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome with neurological manifestations. Plasmapheresis and a phytanic-acid-free diet is advised in Refsum disease. An arginine-restricted diet and oral Vitamin B6 supplementation is used in gyrate atrophy. Acetazolamide may be used for CME associated with RP. Anti-VEGF therapy may be given for choroidal neovascular membranes in Best, Sorsby fundus dystrophy etc.
Newer treatment strategies directed towards stem cell and gene-based treatments are in trials. Luxturna (Spark Therapeutics) provides RPE65gene replacement therapy delivered by viral vectors to restore the visual cycle in children with early stage LCA and has shown promise. Functional cDNA has also been delivered to the retina via viral vectors. With advanced disease or extensive involvement, gene therapy is not effective and pluripotent stem cell transplants or retinal implants may be tried. Subretinal transplantation or intravitreal injections of human embryonic stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelial cells, autologous bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells, undifferentiated umbilical cells etc. are under trial. Application of CRISPR technology with stem cells may allow individualised and targeted treatment.
Retinal prosthetics, e.g., light-sensing microchips are implanted into the retina and transmit impulses via the remaining neural network to the brain. The Argus II Retinal Prosthetic System is one such example. These are used in advanced cases and have had success in restoring some visual perception or improvement in light detection. An intraocular implant releasing ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) has been tried for CSNB.
Dr Soosan Jacob is Director and Chief of Dr Agarwal's Refractive and Cornea Foundation at Dr Agarwal's Eye Hospital, Chennai, India and can be reached at dr_soosanj@hotmail.com