Glaucoma
Virtual Perimetry Reaches More
New virtual reality perimetry system a potentially more affordable alternative to Humphrey field analysis. Roibeárd O’hÉineacháin reports.

Roibeard O’hEineachain
Published: Wednesday, November 2, 2022
GlauCUTU, a new perimetry system that uses a virtual reality (VR) headset and machine and deep learning algorithms, could provide results clinically comparable to those of a Humphrey field analyser (HFA) at a fraction of the cost, according to Visanee Tantisevi MD.
“This novel perimetry system will be beneficial to both the healthcare system and the patients by serving as an applicable and affordable screening tool for glaucoma to prevent delayed diagnosis and treatment,” she said.
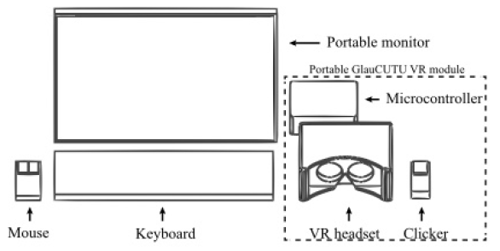
The GlauCUTU system’s VR headset initially presents the patient with the stimulus at its lowest intensity—which gradually increases in intensity until the patient perceives it and presses the clicker. Novel machine and deep learning-derived automated transformation algorithms then convert GlauCUTU sensitivity in seconds into HFA sensitivity in decibel units.
On behalf of her associates, Dr Tantisevi explained their study evaluated the GlauCUTU perimetry system and the new transformation algorithms in 62 eyes of 31 participants. They included 16 eyes of eight glaucoma patients and a control group of 46 eyes of 23 participants without glaucoma. Among the glaucomatous eyes, the defects were early in seven, moderate in three, and severe in six. All participants underwent perimetry using the 24-2 test pattern with both the standard HFA and the GlauCUTU system.
The statistical analysis revealed no significant differences between the visual field index (VFI) of HFA and the VFI of GlauCUTU transformations based on machine learning or deep learning for the entire data set in all stages of glaucoma. The machine learning algorithm of GlauCUTU had the lowest root mean square error (RMSE) and the lowest mean absolute error (MAE). GlauCUTU trained with synthetic data has the highest MAE, which may be due to test-retest variability.
Dr Tantisevi noted the GlauCUTU platform has advantages over HFA in terms of comfort, portability, and expense. For example, unlike the HFA, GlauCUTU’s head-mounted VR device does not require the patient to maintain a fixed head position.
In addition, the average test duration with the GlauCUTU system is less than five minutes compared to 10 minutes with the HFA. That, in turn, helps decrease test-induced eye fatigue leading to more reliable results. The size and portability of the system mean it is easy to transport to rural, under-resourced areas. Moreover, the GlauCUTU system costs around US$1,000, compared to US$40,000 for the HFA device.
“As accessibility to HFA in low-resource countries is limited, a novel VR technology that is portable and inexpensive has the potential to improve glaucoma care in countries such as Thailand,” she said.
Dr Tantisevi added that several studies revealed deep learning has exciting potential in detecting glaucoma. For example, by using archetypal analysis—an unsupervised deep learning approach—it is possible to quantitively and objectively classify regional patterns of visual field loss.
The “archetypes” of the analysis are the extremes of measurement. Research shows eyes with high weighting coefficients for archetypes consistent with advanced glaucoma are also more likely to have high cup-to-disc ratios. Conversely, deep learning models using enface retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) imaging strongly correlate with standard automated perimetry (SAP) quantitative measurements.
“Deep learning could pave the way for future glaucoma screening, particularly in addressing the undetected cases in our communities,” she added.
Dr Tantisevi presented the study during the World Ophthalmology Congress Virtual 2022.
GlauCUTU originated from a collaboration between the Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University and the Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University, Bangkok, Thailand.
Visanee Tantisevi MD is an Associate Professor of Ophthalmology, Head of the Center of Excellence in Glaucoma, and based at the Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand. tvisanee@gmail.com